Executive coaching was developed to help people make the most of their abilities, gain deeper self-awareness, build people skills and resiliency for mastering the challenges of work life. Startup founders, senior management or leaders with significant responsibilities enlist coaches to help them bring new insights and skills to their relationships and broader life picture.
Coaching startup founders through crucial conversations isn’t just serving as a sounding board while they pitch investors, work through co-founder conflict and make hiring and firing decisions as their company scales. Founders undergo a great deal of personal transformation on this journey. They are also responsible for elevating early employees into leadership roles in which they likely have little to no experience. When founders use coaching to learn evidence-based cognitive behavioral tools for personal growth and in their management practices, they internalize a coaching mindset. This leadership style positively impacts the overall health and stability of the organization’s interpersonal climate.
This week while working with a client on communication skill building, she asked me:
“Why are crucial conversations so much harder for some people than others? Giving negative feedback to my employees is the least favorite part of my job as a CEO.” –Startup founder

Here’s a truth I’ve learned from having thousands of therapy and coaching sessions with people about their toughest crucial conversations: everyone experiences heightened, uncomfortable emotions. So unless you’re a psychopath (which is a different article!) it’s not realistic to expect to remain emotionally unchanged when facing high-stakes, crucial conversations. Humans evolved to experience this ‘Fight or Flight’ Response as a survival instinct in the face of perceived threat. When we anticipate having a high-stakes conversations, our brains can get railroaded by our emotions, mimicking the addiction response and diminishing our ability to think critically and generate effective responses. Without developing a practice to manage effectively this pattern, founders are at high risk for making poor management decisions and eventually burnout.
The premise of Cognitive Behavioral Theory is that our emotions are triggered by automatic thoughts that serve to alert us to the possibility of imminent danger. People’s perceptions occur as spontaneous thoughts, which directly influence their emotional, behavioral, and physiological reactions. Our perceptions are often magnified or distorted when they are distressed, making it difficult to see things objectively. By examining our “automatic thoughts” and identifying the factual evidence that refutes them, we are more capable of seeing a view that more closely resembles reality. With practice, our distress will decreases considerably, allowing us to make behavioral choices with higher functionality.
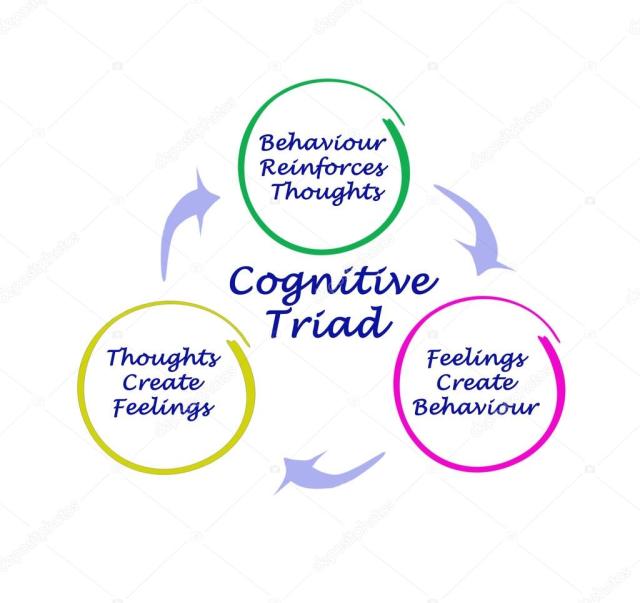
Billionaire investor, author and co-founder of Oaktree Capital Howard Marks discusses risk assessment and the psychology of investing on The Knowledge Project with Shane Parrish. He attributes his success with high-stakes decision-making to his ability to confront the evolutionary emotional programming that automatically drives human behavior. He shares that by adopting a mindset of ‘dispassionate observation and examination of thought‘ before acting, people can learn to accept the impossibility of predicting or controlling the future with 100% accuracy. This mindset reduces the risk of making decisions that overshoot a situation, out of instinctual enthusiasm or fear. In essence, putting cognitive behavioral tools at the helm of his investment decision-making. Founders can use this approach for their toughest, crucial conversations to stabilize their emotions, conserve mental energy and improve the odds of a successful outcome.
How to Use Cognitive Behavioral Tools in Crucial Conversations:
Practice writing out evidence-based thought records to dissect past situations that have lead to uncomfortable feelings. This simple but powerful exercise trains your brain to re-examine how your thoughts, feelings and behaviors are all interconnected.

Practice observing behaviors and listening for the ‘content versus conditions’ of a conversation as a way to spot the risk of a conversation turning into a conflict. The instant people perceive disrespect in a conversation (a hostile condition), the interaction is no longer about the original purpose (the content)- it is now about defending oneself, further escalating emotions.

Our emotional responses naturally turns into a ‘storyline’ or narrative in our head when we perceive hostility that feels like an injustice, shaping how we ‘make meaning’ of the person’s actions. Look for the factual evidence that supports your storyline and identify the emotional response tied to it.
With the understanding that rarely is any situation 100% factually true, look for the evidence that does not support your ‘story’. Practice questioning your conclusions – look for evidence that supports other possible perspectives with the goal of identifying multiple perspectives.

Keep practicing the habit of identifying your emotional response and stories, developing a more balanced point of view rather than accepting your own without question. Learn to understand and take into account multiple perspectives before engaging in crucial conversations. This mindset will translate into more effective exchanges in your relationships, and ultimately help you become a more successful, well-respected leader.

























You must be logged in to post a comment.